Aktuell gibt es keine Themen.
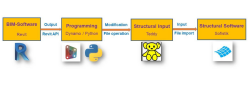
This master’s thesis investigates the exchange between bridge structural analysis and Building Information Modeling using programming languages. The demand for infrastructure projects has grown significantly in recent years, especially in the realm of bridge construction. However, the shortage of skilled labor in this field has caused delays in the necessary development and restructuring of such projects. Furthermore, the workload of today's engineers has become excessive, which presents challenges when faced with the need to accommodate more traffic on bridges. One potential solution is the creation of an efficient dataflow system. This system would involve the highly automated exchange of information between the structural analysis model and other deliverables. By implementing such a system, engineers would be able to streamline their workflows and improve the overall efficiency of the design and construction process. The study defines the information content of construction models in Revit for three common types of bridge families, including frame bridges, and T-beam bridges. The interface for receiving and manipulating the data in Revit is implemented via a script. The data, which is used to generate the Sofistik Teddy-Text files, includes definitions of geometry, materials, and five types of loads. This script semi-automates the creation of the Finite Element model for multiple bridge types. The information is further utilized to export data sheets, providing a quick overview for engineers and clients, as well as list the relevant input values for statical reports. While defining a data pipeline for this manual process, the new system seeks increasing efficiency and behaves more flexible for possible changes in a project. This assists the structural engineer in avoiding the need to consult several documents and repetitively perform the process of planning. The data is also valuable for testing the model and ensuring compliance with guidelines such as Deutsche Bahn, RAB-ING, and others, along with providing additional services outlined in the Honorarordnung für Architekten und Ingenieure, including quantities, costs, reports, etc. The study assesses the possibilities of utilizing the data for other tasks as well. This study evaluates the impact of automation compared to non-parametrized 2D planning methods on projects that involve both single bridge and multiple bridges. The focus is particularly on projects with multiple bridges as automation is believed to have a greater impact on such complex projects. Moreover, The quality of the Finite Element model is assessed by comparing it with the existing Add-Ins available for BIM software. Limiting the scope to a few families aims to generate more consistent mesh structures. In the end, the amount of saved working time is quantified.
Das Bauwesen stellt aufgrund der stetig wechselnden Gegebenheiten vor Ort, dem Einsatz von großen Baumaschinen und einer großen Diversität an Arbeitsumgebungen und Menschen, eine der gefährlichsten Branchen für Arbeitnehmende dar. Zudem unterliegt die Branche einem stetigen Zeit- und Kostendruck sowie Fachkräfte- und Personalmangel. All diese Faktoren kumulieren und verstärken die bestehenden Problematiken beim Arbeits- und Gesundheitsschutz. Mit zunehmender Verbreitung der Verwendung von Building Information Modeling (BIM) steigt auch die Wahrscheinlichkeit des Einsatzes von erweiternden Technologien zur Verbesserung der Arbeitssicherheit. Mithilfe der PRISMA-Methode wurden häufig verwendete Ansätze aus der Forschung und ihre meist genannten Anwendungszwecke ermittelt. Daraus resultierend wurden die exemplarisch lausgewählten Technologien und Forschungsansätze durch Experten aus dem Bauwesen in Form von qualitativen Expert:inneninterviews hinsichtlich ihrer Umsetzbarkeit bewertet und eingeordnet. Die am besten einsetzbaren und vielfältigsten Erweiterungen der BIM Methode stellen laut den Ergebnissen der Expert:inneninterviews Design for Safety (DfS) und das Rule based Checking dar. Nachrangig ist der Einsatz von Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) zu betrachten, aufgrund einer erhöhten Einsatzwahrscheinlichkeit, welche sich vornehmlich auf große Baustellen beschränkt. Auch die Verwendung von Virtual Reality (VR) und Augmented Reality (AR) Technologien erwies sich als schwierig umzusetzen aufgrund technischer Hürden und zu hohen Kosten. Schlussfolgerungen, welche sich daraus ergeben sind, dass ergänzende BIM-basierte Technologien grundsätzlich vermehrt in Betracht gezogen und deren Verwendung vorangetrieben werden sollte, aufgrund der vielfältigen Einsatz- und Verbesserungsmöglichkeiten. Zudem könnten bezüglich der technischen Kompetenzen von Akteur:innen aus dem Bauwesen verstärkt Fortbildungen angeboten und kleinere Unternehmen bei Investitionskosten unterstützt werden, um einen flächendeckenderen Einsatz von Technologien zu ermöglichen. Darüber hinaus sollte ein beidseitiger Informationstransfer von Forschungsvorhaben und -ergebnissen sowie den Bedarfen aus dem Bausektor über verschiedene Kanäle angestrebt werden.
Nowadays, the demand for the electrification of personal mobility has increased. In the automotive industry, development cycles with high-cost pressure have to be managed faster than before with low development costs. Roll-bonded cooling plates are a new production technology in this business. To discuss the manufacturing feasibility of roll-bonded cooling plates, some essential quantities and parameters should be analyzed. In order to evaluate these parameters, two simplified and validated finite element-based models are designed, which can simulate all parts of actual cooling plates. An automisation strategy creates thousands of different models for generating data. After constructing and pre-processing data sets for different quantities, different machine learning algorithms were trained and evaluated on each single data set. A comparison between the actual and predicted results admits that machine learning algorithms could precisely predict the quantities with high R-squared of around 0.9999. Among all algorithms, the extra tree regressor algorithms had the best performance and visualization in all data sets. Finally, a web application is designed, which enables the designer to quickly judge if a design is manufacturable.
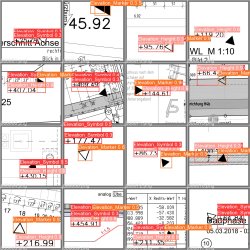
Die Erstellung von Bauwerksinformationsmodellen für bestehende Gebäude kann eine Herausforderung sein. Die Daten sind oft nicht in einem brauchbaren digitalen Format verfügbar. Diese Arbeit verwendet den Deep Learning-basierten einstufigen Objektdetektor YOLOv5, um die Erkennung von Höhenmarkierungen in Bauzeichnungen zu automatisieren. Die Trainingsdaten werden synthetisch erzeugt, um den Mangel an verfügbaren Trainingsdaten zu überwinden. Der Detektor wird erfolgreich auf den generierten Daten trainiert. Zusätzlich werden Techniken zur Datenaugmentierung eingesetzt, um die Leistung des trainierten Detektors zu verbessern. Das leistungsstärkste Modell erreicht einen mAP0,5 von 0,624

Scene understanding from image data aids diverse applications in construction and maintenance. Recently, deep learning models have been employed to extract useful information from visual data at construction sites. These information be used in specific use cases such as site supervision, item detection and material management. One of the most important prerequisites for accurately training a deep learning model and it’s application in computer vision is the availability of a large amount of correctly labelled data. Gathering and labelling large amounts of high-quality photos with the necessary characteristics to train a deep learning model and the diversity can be prohibitively expensive and tedious. Synthetic data can solve both the acquisition and annotation problems of working with visual data. With the existence of modern powerful game rendering engines like Unity and Unreal Engine, these can support the generation of insightful visualizations from synthetic data. Generating realistic images includes environment preparation, noise modeling, and rendering. To address this issue, this thesis focuses on a method for generating high-quality synthetic data that includes the automatic annotation of rendered scenes. The method comprises of four steps: 1) translating 3D model geometries into photorealistic images, 2) automatically annotating the images to generate different synthetic datasets, 3) performing a comparative study on test datasets, and 4) gathering the insights and merging the selected synthetic datasets together to form the final synthetic data set.
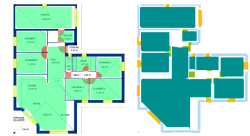
Für die nachträglich Erstellung von 3D-Modellen für bestehende Gebäude werden unter anderem Deep Learning-Modelle genutzt, um Grundrisszeichnung in semantisch besetzte Segmente zu unterteilen. So wird etwa jeder Raum und jede Wand durch eine pixelbasierte Maske repräsentiert. Um diese Segmentierung für die 3D-Modellierung nutzen zu können, muss sie jedoch einer Nachbearbeitung unterzogen werden. Zwei Aspekte dieser Bearbeitung werden in dieser Bachelorarbeit näher beleuchtet: Erstens wird die Pixelregion in eine vektorbasierte Darstellung, d.h. ein Polygon, konvertiert. Zweitens wir das Polygon so nachbearbeitet, dass den zugrundeliegenden Raum bestmöglich abbildet. Für beide Schritte werden mehrere Techniken miteinander verglichen.
In the modern age, the process of designing and planning new buildings makes use of more and more digital tools such as building information modeling and machine learning. For the purpose of training models to perform steps in the process of creating digital models of existing buildings, many raw data points are required, including datasets of floor plan images. Not many such datasets exist and are freely available, and those that do are often small and lack diversity, being gathered from few sources such as architectural offices which generally employ similar styles of drawing and design for all their floor plans. This paper presents a methodology to assemble new and diverse floor plan datasets using web scraping and machine learning. Floor plan images are scraped from the results pages of multiple popular internet search engines. As search engines tend to include undesirable images in their results, the obtained dataset is classified by a machine learning model to detect and remove unwanted images. Multiple models are tested for this classification task and the best performing model is chosen. Analysis of the scraped data shows varying behavior between search engines, with some returning more applicable search results than others. Since the images in the final dataset, consisting of 4.995 images, originate from a multitude of websites, they come in varying sizes, types and styles, forming a dataset more diverse than many comparative ones. Said dataset can, for instance, be used for the creation of machine learning models aiding in the task of digital building modeling, simplifying the creation of new structures. The created dataset could further be enlargened by scraping additional websites or using more search queries, including different languages. Additionally, multiple servers or proxies may be used to avoid encountering bot detection mechanisms and captchas during scraping. The machine learning models may be improved by providing more training data and using random input augmentations to reduce false positive detections.
Der aktuelle Stand der Technik unterstützt die Erstellung von 3D-BIM-Modellen in verschiedenen Softwareprogrammen. Darüber hinaus ist es möglich, Entwurfsanpassungen in den Bauprozess einzubringen und in drei Varianten zu unterteilen: Konstruktions-, Funktions- und Produktvarianten. Mit Hilfe von VR soll der Einsatz des Variantenmanagements visualisiert werden, um Entscheidungshilfen zu geben. Vor diesem Hintergrund widmete sich die vorliegende Arbeit der Evaluierung des Einsatzes von Virtual Reality für das Variantenmanagement in BIM-Modellen. Dabei wurden zunächst die Grundelemente der Arbeit definiert. Im Anschluss daran erfolgte die Visualisierung des 3D-Modells mit den Varianten in VR. Zunächst wurde ein BIM-Modell in der BIM-Software Revit erstellt, dann wurde das Modell kopiert und um die drei Varianten erweitert. Mit dem Unity Reflect Plug-in wurden die Modelle aus Revit exportiert und in Unity Reflect-Review importiert. Dadurch wurden die Modelle in Unity Reflect-Review sichtbar. Auf dieser Grundlage konnte die Unity-Reflect-Review-Toolbox Informationen und die Varianten innerhalb des Modells anzeigen. Denn mit der Filterfunktion konnten die Varianten innerhalb des Modells ein- und ausgeblendet werden. Durch die Implementierung ist die Nutzung der virtuellen Realität für das Variantenmanagement in BIM-Modellen möglich. Der Kern dieser Arbeit ist die Evaluation des Einsatzes. Dementsprechend wurde auf Basis einer empirischen Studie, in der die quantitative Methode verfolgt wurde, ein Fragebogen erstellt, um die Anforderungen und den Nutzen des Einsatzes von Virtual Reality zu evaluieren. Nach den Ergebnissen der Befragung beurteilen die Teilnehmer die Konzeption positiv. Die Software aus der Durchführung erfüllt die meisten Ansprüche und den Bedarf der Befragten.
In Deutschland existieren etwas mehr 40.000 im Bundesfernstraßennetz. Als Baulastträger verantwortet das Land NRW 3812 Brücken auf Landstraßen und 273 Brücken auf Kreisstraßen. Die dezentral gepflegten Zahlen zum Bestand in den einzelnen Kommunen gehen weit darüber hinaus.
Nur wenige dieser Brücke sind digital erfasst. An dieser Stelle bedarf es einer Methode zur Bestandserfassung, welche möglichst effizient und präzise ist. Somit muss die Methode alle Informationen für eine anschließende 3D-Modellierung aufnehmen, über eine hohe Genauigkeit verfügen und mit möglichst geringem Aufwand durchzuführen sein. Im Rahmen dieser Arbeit soll als technologische Basis für die Methode das Laserscanning untersucht werden. Hierzu müssen wesentliche Faktoren guter Bestandserfassung literaturbasiert ermittelt werden. Darauf aufbauend werden Expertengespräche zur Ermittlung von Erfahrungswerten bei der Vermessungsarbeit durchgeführt. Aus diesen beiden Grundlagen wird die Methode zur Bestandserfassung konzeptionell erarbeitet. Unterschiedliche Faktoren (z.B. Zugänglichkeit des Bauwerks) bezüglich der Methodenmodifikation (z.B. Anzahl der Messpunkte) werden herausgestellt und miteinander verglichen. Abschließend erfolgt eine Evaluation des vorgestellten Konzepts anhand eines Brückenbauwerks und seiner Modellierung hinsichtlich des Aufwands und der Qualität, sowie eine Überführung in einen „Best Practice“-Leitfaden.
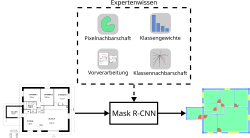
Architectural floor plans can be a valuable source of information to reconstruct digital twins from existing building documentation. In this regard, room geometry and topology, for instance, are essential information to create building models and therefore need to be extracted from drawings. In case the drawings only exist as raster-image files (e.g. from scanning), engineers have to be assigned the tedious task of converting the pure image data into geometrically rich models. Driven by advances in deep learning-based image processing methods and the need to automate the extraction of floor plan geometry, earlier studies successfully subjected floor plan images to semantic segmentation and instance segmentation. This research focuses on potential improvements to these approaches, which are primarily motivated by concepts of informed machine learning (IML), in which expert knowledge is integrated to accelerate the training process and improve inference performance. A baseline Mask R-CNN model is trained on an open-source dataset and is compared to models enhanced with IML techniques. Among others, the effects of (1) a neighboring pixel loss, (2) a weighted cross-entropy loss, and (3) human preprocessing are investigated. Finally, the most promising techniques are combined to train a model which outperforms the baseline by a decent margin. In general, all of the proposed IML techniques improve segmentation results and can be considered in the development of future methods for segmenting floor plan images.
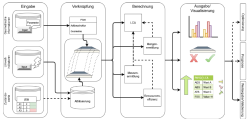
Today much of the data required for processes in the construction industry only exists in analogue form which becomes a problem at a time when more and more work is done digitally. In particular, many tabularly structured documents are often only available in analogue form. This means that the engineer often has to dig through piles of paper until he finds what he is looking for. But even when he finds what he's looking for, he often has to manually convert it into digital form to continue his work, which takes a lot of time. On the one hand, the data can also be scanned, but on the other hand, it is then only available as an image, which makes automatic processing difficult. Additionally, older terms are often used in analogous tables which becomes problematic if you want to search its content automatically. In order to address this problem it is necessary to develop methods that help to digitize these tables. Therefore, this thesis applies several deep learning algorithms to recognize columns and rows in tables. Also, a user interface is developed that makes it possible to extract the data of these tables and search its content based on string matching and, additionally, the underlying semantics which is achieved for a single word by training a word2vec model. In a final step the used algorithms are compared in terms of their accuracy and their hardware requirements.
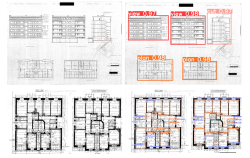
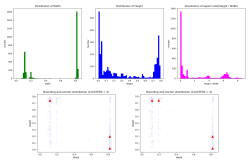
Artificial Intelligence is becoming more prominent each day. Many fields try to implement it in their workflow. With the increase in the importance of Building Information Modelling, there is a need to have information about construction projects in digital form. While being some of the oldest forms of documentation for buildings, 2D plans contain a lot of information that is of great use, especially in the case of as-built plans. Several attempts have been made to extract information from 2D plans in an automated manner, some of them including Artificial Intelligence. While some researchers have used synthetic data to train Deep Convolutional Neural Networks for automatic extraction of information from 2D plans, others have used existing plans. This work aims to extract information from old scanned 2D plans using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks and in this manner to try and get an understanding of how Deep Learning manages this scenario. A comparison between different Neural Network architectures is conducted and an image-slicing method is explored, to detect small objects. Furthermore, a hyper-parameter tuning strategy is conducted in order to get the best combination possible between them. Lastly, a Microsoft Excel file is created to present the information extracted and a simple Flask Web App is built, in the form of a proof of concept.
Der Bausektor ist einer der ressourcenintensivsten Sektoren und verantwortlich für einen beträchtlichen Anteil des Energieverbrauchs, der Treibhausgasemissionen und der Bindung von stark nachgefragten Rohstoffen. Daher ist es die Aufgabe des Bausektors, die Klimaziele zu erreichen und den Ressourcenverbrauch von Baumaterialien zu reduzieren. Gerade der Infrastrukturbereich, und hier insbesondere der Straßenbau, leistet dazu einen wesentlichen Beitrag. Durch eine ganzheitliche Betrachtung des Lebenszyklus von Baumaterialien können die Umweltauswirkungen quantifiziert und gemessen werden. Auch wenn die Digitalisierung und die Anwendung der BIM-Methodik (Building Information Modeling) im Straßenbau stetig voranschreiten, ist ihr Anteil derzeit noch begrenzt. Daher befindet sich auch die Integration von LCA (Life Cycle Assessment) in die BIM-Methodik noch im Anfangsstadium. Vor diesem Hintergrund wurde eine Methodik entwickelt, die eine automatisierte Ökobilanz für parametrische Straßenstrukturen durchführt.
Cracks in concrete and rusting reinforcing steel can pose a critical threat to the stability of buildings. Therefore, reliable detection of these damages as part of maintenance plays an important role in ensuring the safety of civil infrastructure. Conventional image processing-based methods are set to one damage type and lack the adaption to new environments in real world-situations. By using images from mobile devices this thesis presents a comparison of three convolutional neural network architectures to locate and classify the mentioned damage types. Two datasets were created for this task and varied by applying Data Augmentation. For classifying images with a 227×227 pixel resolution a 98.03% f1-score was achieved. In a second step, the networks were transformed to fully convolutional networks and applied to images of different aspect ratios. Thereby, the proposed method has successfully achieved a f1-score of 96.28% in classifying cracks and corrosion. The segmentation of the images on a grid level can further be used for the digitalization of the damages.
Building Information Modeling (BIM) beschreibt eine neue Art der digitalen Planung und Verwaltung eines Bauprojekts und kann darüber hinaus zur Verwaltung relevanter Daten während der gesamten Nutzungsdauer des Gebäudes verwendet werden. Im Vergleich zu einem herkömmlichen Planungsprozess werden bei BIM mehrere Arbeitsabläufe zu einem einzigen zusammengefasst, was wiederum das Fehlerpotenzial verringert, die Zusammenarbeit zwischen den Beteiligten verbessert und die Effizienz insgesamt erhöht. Während das oben Gesagte für einfache Gebäude sicherlich weitestgehend zutrifft, gilt dies nicht für die Planung von Infrastruktur-projekten, wo der Einsatz von BIM noch erweitert und weiterentwickelt werden muss, um sein volles Potenzial auszuschöpfen. Zu Beginn dieser Arbeit wird ein Überblick über den derzeit praktizierten Workflow gegeben, wobei der Schwerpunkt auf den aufgetretenen Problemen liegt. Das größte Problem ist das Fehlen einer generischen Konvertierung zwischen dem BIM-Modell, das für die Planung verwendet werden soll und der statischen Abstraktion, die für fortgeschrittene Finite-Elemente-Analyse (FEA) benötigt wird. Anschließend wird ein neues Datenformat, das sich noch in der Entwicklung befindet, auf seinen aktuellen Stand und seine Implementierung in bestimmte BIM-Software untersucht. Das Hauptziel des Interface ist es, das fehlende Bindeglied zu schließen und somit jedes geometrische Modell auch ohne die manuelle Implementierung spezifischer Komponenten strukturell untersuchen zu können. Im praktischen Teil dieser Arbeit wird ein komplexes Widerlager entworfen und analysiert. Das oben genannte Datenformat wird zur Generierung der entsprechenden statischen Abstraktion verwendet und nach vorgegebenen Kriterien wie Zuverlässigkeit und Zeiteffizienz untersucht. Damit wird die Möglichkeit zur einfachen Berechnung fortgeschrittener geometrischer Modelle nachgewiesen. Diese Ergebnisse lassen den Schluss zu, dass der verbesserte Workflow für die gesamte BIM-Entwicklung von Nutzen sein wird.
Aufgrund von steigenden Achslasten und dem ständig wachsenden Schwerlastverkehr im Bundesstraßennetz, steigt auch der Erhaltungsbedarf im Bundesfernstraßennetz. Mit Pflichteinbindung der BIM-Methodik im Infrastrukturbau ist ein 3D-Modell als Grundlage für die Nutzung der Methodik in allen Lebenszyklusphasen vorausgesetzt. Für die Infrastrukturbauwerke liegen jedoch nicht immer Bestandsmodelle vor. Moderne Vermessungstechniken ermöglichen bereits eine aufwandsarme Erfassung eines Bestandsobjekts. Darunter das Laserscanning mit dem Ergebnis einer Punktwolke. Punktwolken dienen als Informationsquellen, wobei sie Abmessungen des Bauwerks beinhalten. Die Überführung der Geometriedaten in ein digitales BIM-Modell ist jedoch weiterhin ein recht aufwändiger Prozess. Unter Zuhilfenahme von KI-Methoden soll dieser Prozess automatisiert werden. Dabei werden Methoden aus dem Bereich des Machine Learnings verwendet, die das Generieren von Flächen aus einer segmentierten Punktwolke ermöglichen. Die Segmentierung der Punktwolke wurde dabei als vorausgesetzt angenommen. In Hinblick auf die Rekonstruktion, werden verschiedene Unterkategorien des Anwendungsfallsder Bestandserfassung und -modellierung aufgezeigt und die dazugehörigen Anforderungen formuliert. Abschließend wird eine Benchmarkmethode aufgestellt, um die KI-Methoden miteinander zu vergleichen. Hinsichtlich der Rekonstruktion der Punktwolke sind keine Geometrien zu erwarten, die mit semantischen Informationen angereichert sind. Stattdessen werden Flächen als Ergebnisse berechnet, mit denen im Nachgang eine teilautomatisierte Rekonstruktion der Punktwolke ermöglicht werden soll.
Im Stufenplan „Digitales Bauen und Betreiben“, initiiert durch das Bundesministerium für Verkehr und digitale Infrastruktur (BMVI), wird die Anwendung von Building Information Modeling (BIM) in Großprojekten ab 2020 verbindlich vorgeschrieben. Insbesondere öffentliche Auftrag-geber setzen dabei auf die Methodiken des „openBIM“ unter Zuhilfenahme offener Datenformate. Im Zuge der geplanten Einführung der BIM-Methodik im Dezernat 5.2 Baumanagement der Ruhr-Universität Bochum soll eine umfangreiche Anforderungsanalyse insbesondere der Austauschbeziehungen und der Nutzung von Gebäudeinformationsmodellen durchgeführt werden. Relevante Anforderungen und Prozesse werden durch Sichtung von bereitgestellten Dokumenten, Interviews und weiteren zweckdienlichen Methoden erhoben und dokumentiert. Auf Basis der erhobenen Informationen wird ein idealtypisches openBIM-Einsatzszenario abgebildet, bei dem der Einsatz eines Information Delivery Manual (IDM) validiert wird.
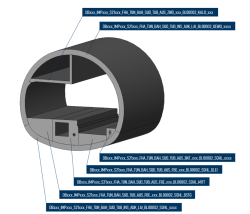
Um die flächendeckende Verwendung von BIM im Bauwesen voranzutreiben, sind Richtlinien und Standardisierungen zu schaffen, die einen effizienten Umgang mit Modellen ermöglichen. Die Entwicklung von Datenkatalogen und Objektvorlagen ist hierbei ein wichtiger Schritt für standardisierte Modelle, die sich praktikabel in unterschiedlichen BIM-Anwendungsfällen nutzen lassen und die notwendigen Informationen liefern. Der DAUB hat mit der Empfehlung Digitales Planen, Bauen und Betreiben von Untertagebauten –BIM im Untertagebau und mit der zugehörigen Ergänzung Modellanforderungen–Teil 1 eine allgemeine Modellierungsrichtlinie sowie einen Datenkatalog für Modelle im Untertagebau veröffentlicht. Darin werden eine allgemeine Projektstruktur und Regeln zur Objektcodierung vorgegeben. Der Datenkatalog beinhaltet Objekte und relevante Merkmale des Untertagebaus und soll damit eine Modellierungsgrundlage für Modelle bereitstellen. In dieser Arbeit werden die Modellierungsrichtlinie sowie der Datenkatalog in der Anwendbarkeit geprüft. Dazu werden die Vorgaben auf Tunnelmodelle eines realen Projekts angewandt. Mit diesen werden ausgewählte BIM-Anwendungsfälle durchgeführt, um die Praxistauglichkeit der Vorgaben anschließend zu bewerten. Ein weiterer Aspekt der Arbeit beschäftigt sich mit der allgemeinen Struktur des Datenkatalogs und bewertet ihn hinsichtlich Interoperabilität. Dazu werden die Interoperabilitätsanforderungen der ISO 23386:2020-03 als Grundlage herangezogen.
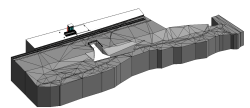
Seit einigen Jahren hat sich der Begriff BIM in der Baubranche stark durchgesetzt. Diese Methode wird heute insbesondere in Hochbauprojekten angewendet. Auf Grund ihrer Komplexität sind Ingenieurbauwerke dagegen eine besondere Herausforderung für die Anwendung der BIM Methodik. Die vorliegende Arbeit setzt sich mit der Planung eines reellen Ingenieurbau Projekts auseinander.
Sperrvermerk
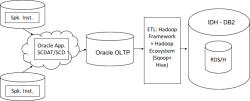
Intelligente Technologien für Unternehmen gelten heute weltweit als einer der vielversprechendsten Bereiche des IT-Marktes. Es ist daher wichtiger denn je, die gespeicherten Daten und Informationen schneller zu verwalten. Im Konzept von Big Data spielt Data Warehousing eine wesentliche Rolle, da dadurch Prozessoptimierung, -analyse und -verbesserung sowie Datenmanagement entwickelt und realisiert werden können. In dieser Arbeit wurden sowohl die Business Intelligence als auch Big Data und das Data Warehouse (DWH) und deren ETL-Prozesse (Extraktion, Transformation, Laden) konzeptionell beschrieben. Der Fokus dieser Arbeit liegt auf der Untersuchung und Umsetzung der Möglichkeiten zur Optimierung von DWH-Services, Datenanalyse und Datenmanagement. Dazu wurde die Firma Finanz Informatik GmbH und deren implementierte DWH-, Datenmanagement- und Datenbereitstellungsmethoden betrachtet. Die allgemeinen Methoden zur Optimierung eines DWH und des damit verbundenen Datenmanagements wurden ebenfalls diskutiert. Der Hauptteil der Masterarbeit umfasst die detaillierte Analyse der Anforderungen der Finanz Informatik GmbH aus technischer und fachlicher Sicht sowie die Untersuchung und den Vergleich der in diesem Zusammenhang üblichen Untersuchungen. Nach der Priorisierung und der Analyse werden einige der Optimierungsmöglichkeiten modelliert und sowohl konzeptionell als auch logisch umgesetzt. Anschließend wurden die Umsetzungen getestet, mit dem Kriterienkatalog verglichen und bewertet. In dieser Master-Thesis wurde gezeigt, dass durch den Einsatz von Optimierungs- und Datenmanagement-Methoden die Performance eines DWHs verbessert und das Datenqualitätsmanagement gesteigert werden kann.
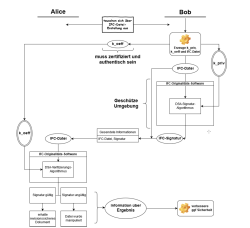
Der technologische Fortschritt macht auch vor der Baubranche nicht halt: Das Building Information Modeling (BIM), das für die Bauplanung genutzt und über IFC-Dateien beschrieben wird, boomt in Deutschland. Die von der Bundesregierung geförderte und entwickelte Plattform BIMSWARM will diese Digitalisierung des Bauwesens auch für kleine Unternehmen erschwinglich machen. In der Folge werden immer mehr IFC-Dateien in Auftrag gegeben und der Planungsprozess von Gebäuden wird langfristig revolutioniert. Es wird auch neue Anforderungen an den Schutz vor Angriffen und Manipulationen dieser Dateien geben, um Unternehmen fehlerfreie und sichere Baupläne zu garantieren. Im Rahmen dieser Bachelorarbeit wurden verschiedene Ansätze und Methoden für die Originalitätsprüfung von IFC-Dateien recherchiert und vorgestellt. Anschließend wurde eine Methode anhand umfassender Kriterien ausgewählt, mit der eine Prüfsoftware implementiert werden kann. Weiterhin wurde ein Konzept für den Ablauf und die Architektur der geplanten Software entworfen, die schließlich auf der BIMSWARM-Plattform zur Verfügung stehen wird. Bei erfolgreicher Umsetzung wird es möglich sein, die Integrität und langfristige Sicherheit von IFC-Dateien im Zusammenhang mit BIM auch auf rechtlicher Ebene zu gewährleisten.
Da die Bauprojekte immer umfangreicher und die Arbeitskräfte immer teurer werden, gewinnen die Informatisierung und die Digitalisierung im Bereich Architektur, Ingenieurwesen und Bauwesen (AEC) immer mehr an Bedeutung. Die Verfügbarkeit der BIM-Methode (Building Information Modeling) bietet der Bauindustrie eine hervorragende Möglichkeit, Leistungsstufen digital zu dokumentieren und automatisch im Detail zu berechnen. In Kombination mit der Blockchain-Technologie kann nun eine revisionssichere Dokumentation und ein Informationsaustausch in Echtzeit erfolgen. Hierdurch können verschiedene Anwendungen im Bauwesen unterstützt werden. Dazu gehören die Liefer- und Abnahmeprozesse bei der Finanzierung von Projekten, die Koordination der Planung, die Abrechnung von Bauleistungen oder der Gebäudebetrieb. In dieser Arbeit wird zunächst die bestehende Forschung zur Einführung von BIM- und Blockchain-bezogenen Konzepten analysiert. Dann führen wir eine Designforschung mit einer prototypischen Implementierung durch, um ein Demosystem für den Betrieb von 5D-BIM-basierten Daten in Blockchain zur Digitalisierung von Bauprozessen vorzustellen. Schließlich diskutieren wir verschiedene Aspekte, die in Zukunft verbessert und weiterentwickelt werden können.
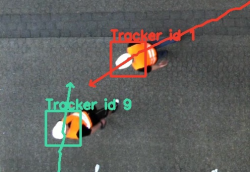
On construction sites workers are exposed to several dangers. Especially cranes are considered dangerous, because they can potentially cause accidents by being struck by crane load. In the worst case they cause fatal injuries. It is necessary for crane operators to know the location of nearby coworkers. By improving communication among workers and crane operators it is possible to reduce the risks of accidents. An automated system specialized in warning and signalizing potential dangers could prevent further casualties.
By using cameras that can be attached to cranes this thesis presents a method for tracking workers. Considering the implementation of methods in the fields of computer vision and machine learning the tracking system is established. The tracking process is structured in three phases. To isolate objects and persons the first phase separates for- and background using a background subtraction. Using the soft cascade method trained to detect worker the second phase classifies isolated regions in the foreground. Finally, using the kalman-filter workers will be tracked.
Results are evaluated by analyzing roc-curves to detect a nearly optimal classifier. Manually marked images are used to compare against the detection and valued. Those results can then further be used to evaluate the efficiency of the tracking system.

Augmented Reality (AR) is a novel technology, which is mainly in the state of research and rarely used in practice, especially in construction. In order to point out the capability of deployment and the potential fields of AR technology in the construction industry, this master thesis focuses on the technical experience of construction engineers. Different points of views and improvement suggestions are provided through interviews with those experts, who have worked on various construction projects. The challenges from construction projects and suggestions of deployment with AR are pointed out. Based on the evaluation of the experts’ suggestions, an application prototype with AR is developed to solve a practical problem and provides an example of the usage of BIM data with AR. The test of the prototype is carried out by the interview partners. The judgment of the prototyp as well as the usage of AR in the construction practice is worked out from the feedback of the test persons. Finally, the possibilities and challenges of the usage of AR technology in the surroundings of construction are discussed.
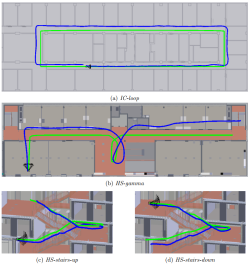
The ability of indoor pose estimation is an essential key component for a wide range of applications in the construction industry, such as progress monitoring of finished works or augmented reality-based maintenance and navigation of indoor facilities. There are numerous indoor localization methods based on different technologies, with an image-based approach via a mobile device being the most economical. This work aims to investigate an existing image-based approach using convolutional neural networks trained on synthetic images to estimate the pose of real images. Four datasets of indoor scenes from two buildings with various trajectory properties were created and independently analyzed. The average position accuracy was 11m, while an accuracy about 1m could be achieved by training and testing the artificial neural networks with a dataset from the same domain. Moreover, the networks using cross-domain data localized all test images in a confined area and estimated the orientation mostly as the same one.The ability of indoor pose estimation is an essential key component for a wide range of applications in the construction industry, such as progress monitoring of finished works or augmented reality-based maintenance and navigation of indoor facilities. There are numerous indoor localization methods based on different technologies, with an image-based approach via a mobile device being the most economical. This work aims to investigate an existing image-based approach using convolutional neural networks trained on synthetic images to estimate the pose of real images. Four datasets of indoor scenes from two buildings with various trajectory properties were created and independently analyzed. The average position accuracy was 11m, while an accuracy about 1m could be achieved by training and testing the artificial neural networks with a dataset from the same domain. Moreover, the networks using cross-domain data localized all test images in a confined area and estimated the orientation mostly as the same one.
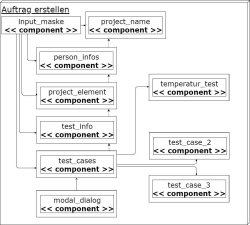
The Bosch Rexroth company in Dortmund has various test benches to test different types of gears used in agricultural machinery. The test benches are managed by different employees, so that an order must be created for the use. To get an overview of the orders, test stands and gearboxes used, an application that contains a suitable user interface and a data storage system must be developed. This bachelor thesis describes the conception and implementation of such an application, which we call the Data Aggregation Tool (DAT). Important aspects of planning in combination with agile project management, mockups and prototypes, as well as the implementation of different components, are discussed using the Framework Angular. Requirements for the application are defined with use cases and user stories. Different orders are divided into different categories, with one being considered complex enough for all other orders to build on. To test the implementation of the application, a limited evaluation is performed and evaluated.
Up to the present, only analogous applications for construction permit (ACPs) are accepted in Germany. Yet the submission of a digital ACP provides several advantages, especially when making use of existing federal standards in the areas of construction and planning. Further, the direct integration of Building Information Modeling (BIM) into a digital ACP process provide further potential. Within the scope of the ongoing research project "BIM-basierter Bauantrag" (BIM-based ACP), which aims to integrate BIM into the digital ACP process, one objective is the development of a software prototype suitable for realizing a BIM-based ACP process. An existing Desktop-based prototype already provides basic functionality. A web-based solution would offer further advantages, such as platform independency and centralized data environments. This work examines the migration of the existing Desktop application into a web-based environment. In order to be able to perform such a migration, this work provides an extensive requirements analysis. The migration's primary objective is to carry over as many software components into the new system as possible to minimize code changes. In order to achieve that goal, an appropriate strategy has been designed to develop a web-based client which reuses parts of the existing software as server-components. The resulting web-based software system has been evaluated using a real-life sample project.
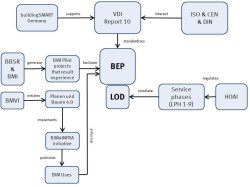
Project management and construction informatics had begun to blend and guide the construction industry internationally the last decade. Technological advancement gave naturally birth to the innovative Building Information Modelling method on the construction scene. With the introduction of a BIM Execution Plan, a company develops an agenda that describes all the steps of generating a project, clarifying the project goals and its coordination throughout the whole life-cycle of the structure. The expansion of the thesis is twofold. Namely, in the first part describes in detail the pure theoretical background of BIM Execution Plan and its adaptation on the company by a development of a Master BEP Format and a second task of a computational implementation method to automatize the quality control of buildings. The main aim of this scientific work within a Consulting Design in Construction Management business is to deliver the knowledge and enlighten the co-workers for the applied management tools of BIM that the market offers nowadays, as well as to advance the work-flow on BIM Uses that constitute a BIM Execution Plan’s input. The master thesis has been achieved by an elaborate literature and regulations review, whereas a continual use of the company’s provided software was assigned in order to realize the shortcomings on a genuine project. Moreover, an intense practice in Integrated Development Environments and programming languages was attained and ultimately a quality control tool for Revit Autodesk was implemented.
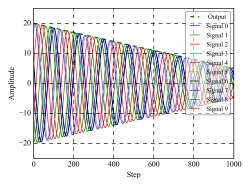
As self-driving technologies are implemented in autonomous vehicles an increase in the reliability on automotive electronics hardware is increasingly becoming a requirement. Current methods have statistical significance; this mean that they remain population-relevant and are prone to outliers. A new way to increase the reliability of automotive electronics systems and getting it closer to a 100% is to implement PHM. This would imply the presence of degradation sensors included in the silicon of the packages, enabling a more direct measure of quantities related to the degradation of the system. This thesis focuses on the development of three Machine Learning models for the prediction of degradation of electronic components. A data set is created from ETVs subject to accelerated ageing. This data is transformed to a compressed understandable form with various preprocessing techniques and then fed to the ML models. After tuning, the best model is picked and applied to new datasets. Expert knowledge from Bosch is used to validate the results at every stage. After having proved that the concept is valid, new models are developed using only a small dataset of ANSYS thermo-mechanical simulations data performed by Bosch and provided to the author and then used for prediction of real-world experimental stresses.
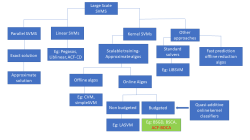
Support Vector Machines (SVMs) are popular machine learning methods, especially for binary classification of data. Computational complexity of kernelized (Non-linear) SVMs becomes a limiting factor when dealing with large-scale machine learning problems. This thesis presents an online adaptive version of Dual coordinate ascent that honours a budget constraint and restricts the number of support vectors used to represent the model. This new algorithm is coined as Adaptive coordinate frequency budgeted
stochastic coordinate descent (ACF-BDCA). The Budget methods have proven to be effective for reducing the training time of kernel SVM while retaining high accuracy. In addition to that, instead of fixing selection frequencies of a general Coordinate ascent with uniform random selection of coordinates, the Adaptive coordinate frequencies (ACF) method removes the need to estimate optimal coordinate frequencies beforehand, and it automatically reacts to changing requirements during an optimization run. The ACF-BDCA algorithm has demonstrated the ability to significantly speed-up the BDCA method. Also, a new robust stopping criterion was successfully designed to halt this non-convex optimization problem, while achieving good performance levels.
The integration of mechanical and electrical building equipment may cause issues and leads unquestionably to an increased complexity of the entire building process. Especially the planning of openings for technical equipment is a very complex procedure. The usage of classic methods for the coordination of openings between all the involved parties of a construction process causes inconsistencies and intransparency, as simultaneous work is not possible. Building Information Modeling (BIM) aims at providing appropriate means to tackle the challenges, thereby improving the overall transparency and quality. Coordination and communication during the planning of openings is possible because suitable BIM-based tools are already available. Despite its many benefits, however, the processes are too complex and deficient, especially when different data formats of opening-models have to be reconciled. This master thesis develops suitable processes for a significant improvement of the model-based planning and coordination of openings. Hereby the loss of information through different data formats will be compensated. By using the open BIM Collaboration Format (BCF), the transparency and traceability of coordination and communication processes is ensured.
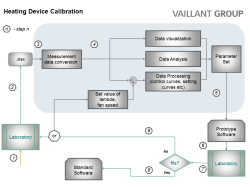
As a result of the mechatronization and the exponential growth in the number of product variants, the calibration effort of heaters is expanding intensely and demands new, more efficient approaches other than experimental laboratory testing. Within the scope of the present master thesis, an application tool was developed, the tool which is modular in design and was implemented based on the UI/UX concept so that the user can operate it intuitively, can be systematically used by a device development engineer to read, visualize and process measured data in order to automatically calculate functional parameters of a heating device.
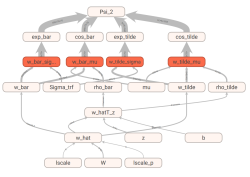
In the recent years a lot of new models have been developed in machine learning. One of such new model classes is Deep Recurrent Gaussian Process. In this thesis we de scribe the Deep Recurrent Gaussian Process with Variational Sparse Approximation, in particular the one presented by R. Föll, and make an attempt to provide a time and memory efficient implementation for it, in order to ease its practical application. We implement this model in two different packages, TensorFlow and PyTorch, supply as a result three implementation versions and indicate some issues that have arisen in the meanwhile. We further evaluate performance of our code and compare all three implementations in terms of system memory requirements and running time, estimating the most balanced one to be about 4.2 times faster and with no increase of system memory consumption, compared to initial implementation presented by the model’s author. Also, a brief estimation of model’s accuracy based on comparison with other Gaussian Process based models is made.

There are several service building components (SBC) like fire extinguishers and emergency exit sings in public buildings. Since they usually possess a prominent appearance and their locations are known, they can be used for indoor navigation. This thesis deals with a color-based preprocessing of images containing SBCs for a subsequent detection. The goal is to find relevant image patches, that may contain SBCs and, this way, reducing the search space within the image that needs to be examined for further object recognition. To achieve this, a dataset has been created which consists of fire extinguishers, fire alarm boxes, smoke funnel boxes and emergency exits. Since these SBCs possess salient colors, an object segmentation by color is reasonable to facilitate detection. For segmentation, each component's color range is determined by averaging over several samples. Segmentation is, then, performed in different color spaces in order to find the optimal color space by comparing the results. The HSV color-space demonstrated acceptable results across all objects but emergency exits. The LAB color-space shows the best results for emergency exits, however requires a vastly bigger runtime for the segmentation.
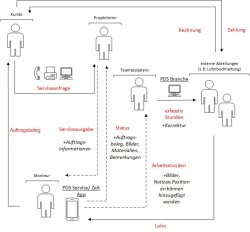
As a result of digitization, an increasing number of small and medium sized companies are forced to design and optimize internal operating processes. This is being accomplished with the help of today's intelligent technologists according to the vision of Industry 4.0. The present scientific work analyzes the state of digitalization in the craft industry. In this context, PDS, a craft specialized ERP System, is evaluated in Elomech Elektroanlagen GmbH as a practical example of how the software links internal processes with each other and thus optimizes the processes in the company. The focus of analysis is on the mobile applications of PDS Service App and PDS Zeit App, which enable the mobile administration of service orders and the digital recording of hours. Despite the gain of efficiency, the analysis shows that there are still existing challenges and risks for the company. In particular, issues regarding the privacy aspect of fitters needs to be a critical consideration.
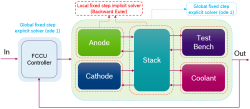
Real-time performance of fuel cell plant model developed in Simscape is evaluated and tested in this thesis. Various simulation models for fuel cell system are developed by different departments at Robert Bosch GmbH in various simulation platforms for e.g. Simscape, GT-Power. A matrix is developed for comparison of these simulation models based on different criteria like model type (0-D or 1-D), accuracy, validation, parameterization, parameter identification and modeling physics (physics based, data based and hybrid). Besides exploring the configurations of model like solver type, step size and usage of local solvers, built in performance packages of Simulink (e.g. Simulink profile report, Performance Advisor) are also used to further check the computationally intensive parts of the model in Simulink environment. It is observed that the execution time can be optimized by selecting a local solver and fixed-cost runtime consistency iterations on Simscape model. Later on different experiments were performed on Simscape fuel cell model on ETAS Labcar RTPC in Hardware-in-the-Loop environment to test the real time performance.
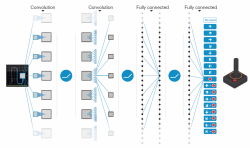
This thesis deals with the application of the Deep-Q-Learning method for a collision-free drone flight. Building on Reinforcement Learning, the aim is to use a drone as an "agent" by interacting with the environment using rewards or punishments. The goal is to teach a behavior to enable a collision-free movement through 3D space. To explore this, the realistic simulation environment AirSim is used where the real world is adequately represented. The drone can be controlled via a Python programming interface to interact with the environment according to physical laws. Depth images of a virtual camera attached to the front of the drone map the environment and are passed as input to an artificial neural network.
Traditional working practices of quantity and cost determination, which are still common in the construction industry, are characterized by a susceptibility to errors and time intensity due to their manual approach. Concerning this matter, the working methodology Building Information Modeling (BIM) offers a process optimization, which promises the avoidance of laborious and error-prone work by a consistent further use of digital information, resulting in an increase in quality and productivity. In the construction industry, engineering structures e.g. bridge and tunnel construction have different requirements compared to classical building structures, which ultimately also affect the implementation of BIM. Within the scope of this work, it was possible to develop a concept for an optimized BIM-based cost calculation in this field. As a result, workflow processes were used to describe the necessary work steps, roles and responsibilities as well as exchange formats for three application-specific scenarios relating to the building model and the cost structure. Finally, the feasibility of the concept was prototypically demonstrated using selected software products.
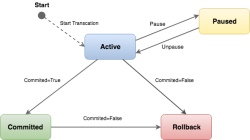
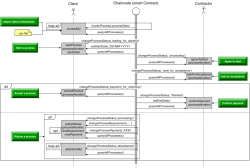
Transactions help to create reliable software and bring consistency and integrity to the system. Each transaction has to be completed successfully or aborted in the case of failure. Distributed transactions have the same properties of transactions and are a set of two or more transaction branches, which can span multiple data sources. The Vendo project is the process of booking Deutsche Bahn train tickets online per website or per “DB Navigator”, or via ticket vending machine. The project consists of various RESTful microservices. For each request of the user, a transaction will be generated. Each transaction has a transactionId and will be continued until the end. Implementation of transactions in such a large project can be tricky and presents some challenges. The goal of the thesis is to identify these challenges of implementing the transactions in Vendo project, find appropriate solutions for them, and monitor the transaction at the end to ensure that they work.
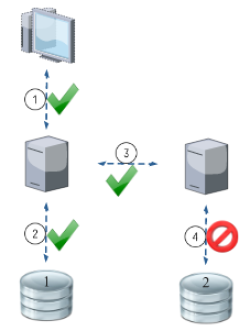
This work examines the various aspects in the development of a software application based on the architectural model of microservices und the expected benefits. Particular attention should be paid to compliance with data consistency in relational databases, through which transaction security must be addressed. For revision, a suitable prototype has been implemented. The architectural pattern "microservices" requires an unusual amount of communication over an insecure network (the Internet). Therefore, the risk of a network failure must be considered.
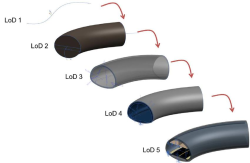
The focus of this thesis is the development of a LOD concept for 4D and 5D analysis using BIM for bridge structures. Such a LOD concept determines the geometric and semantic structure, where the levels of detail are to be defined and specified by specific parameters. Relevant requirements flow into the development of the LOD concept as well as the rules for scheduling and cost planning. Subsequently, a prototype implementation of the LOD concept using a workflow is presented.
The roads and streets of Germany extend over a length of approximately 230,000 km must be continuously monitored and maintained. Both the age of many roads, dating back to the 1970s and 1980s, as well as the high traffic load of today force the road authorities to plan conservation measures using digital tools. In particular, the easy exchange of data required for road maintenance from the start of a repair project to the final phase between all involved is an important aspect. The benefits anticipated from the use of digital planning methods in road maintenance lead to increased efforts to further development of digital computer-aided methods.
Due to the technological advances of computer-aided work processes, the method Building nformation Modeling (BIM) as a digital planning method based on 3D-models by now basically determines the developments in the construction industry. Since at least the publication of the graduated scheme „Digitales Planen und Bauen“ by the Federal Ministry of Transport and Digital Infrastructure, and therefore the requirement of a solid BIM-level for new infrastructure construction projects after 2020, standards and guidelines for the implementation of the BIM-methodology are urgently needed in bridge construction. The BIM-applications in different project phases differ both in terms of their requirements for model detailing and in the implementation of subject-specific analyzes. This is where the concept of the Level of Development (LoD) comes into play, which defines the level of detail of the digital building model in different requirement stages and ensures sufficient nformation content for the specific analyzes.
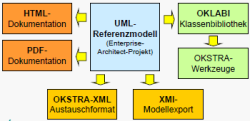
Road maintenance and restoration have undoubtedly the largest need of funding within the road infrastructure. Therefore, the careful planning of maintenance measures for roadways has extraordinary relevance. In particular, BIM systems have gained significant importance in engineering disciplines because they allow the linking of data and their dependencies in a data model. On the one hand, a high volume of data can be processed while, on the other hand, information can be specified in great detail. In maintenance planning, the OKSTRA standard is currently being used. As a result, a BIM-suitable data model for road construction based on the OKSTRA is discussed in this thesis.
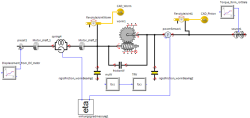
This thesis presents an efficient best-effort approach to improve the simulation performance of a given virtual prototype of Electric Steering Column Lock Assembly (ESCLA) to make it real-time capable. This prototype is modeled and simulated in SimulationX software. While reducing the model, balance between accuracy and performance is maintained. Since it involves mainly mechanical and electrical components, special importance is given to capturing the associated physical events as far as possible. Subsequent use of such kind of reduced simulations is for the purpose of Model in Loop (MiL) testing of the components.
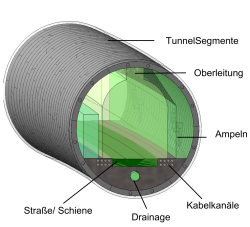
The need for Building Information Modeling (BIM) in the field of infrastructure engineering has never been greater. BIM is slowly but surely spreading worldwide and can be the game changer in the AEC (Architecture, Engineering & Construction) industry. The federal ministry of transport and digital infrastructure in Germany wanted to ensure, that digital planning and building will be established for the German AEC industry as well. Therefore, they introduced a roadmap for Digital Planning and Construction (Digitales Planen und Bauen) back in 2015, that aims at the standardization of Building Information Modeling within the infrastructure until 2020. Currently, research and experience from real projects are showing, that unified guidelines and standards should be defined for a successful use of the BIM method. For example, a definition of a geometric and semantic information depth of a digital model is for the building section with terms like Level of Development (LOD) internationally established. During this study, a concept for the description of Level of Development of tunnel structures with mechanical propulsion is developed.
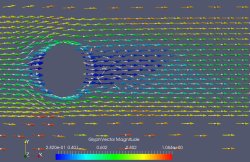
Numerical simulation for fluids, commonly called Computational Fluid Dynamics(CFD), has become standard tool for a wide range of industries. With the expansion of computing power demands for the physical accuracy, spacial and temporal boundaries of fluid simulations have increased. The common bottlenecks for numerical modeling fluids, include: large run times, computational power and expertise required. One novel solution that has been proposed to reduce the large run time is through the generation of black-box CFD surrogate models. This paper focuses on exploring the concept using Machine Learning methods to generate a CFD surrogate model to replicate entire simulation results. The novel concept of CFD surrogates was first reviewed by looking at the prior research. From an in depth review common strategies were determined and evaluated through experimentation.
The rapid growing interest in working conditions with Building Information Modeling (BIM) raises the question, which processes can be realized with the available BIM-tools. To answer this question, this bachelor thesis will observe a geometric presentation of a tunnel which was created by a shield driving, to make a belated valuation of the installation quality. The geometric presentation is based on a modeled ring which will be placed on a three-dimensional track by using a parametric model. The modelling and the parametric model will be done by Revit and Dynamo, two programs from the company Autodesk. With the help of the ring modelling and the implementation with the model, a qualitative assessment methodology is put up to judge the situation exactness of tunnel driving afterwards. The feasibility and suitability of the methodology is checked with the help of a real use case.
In order to improve existing 3D models of urban environments the structure of facade elements and windows in particular is of high interest. Therefore, the problem of automated extraction of window locations from facade images is to be solved using methods of computer vision. In this approach a cascaded classifier is implemented and trained with various window examples. This classifier is used to detect windows in any presented image without requiring user intervention. The evaluation of it proved the trained classifier functioning properly. Further optimizations to allow for a more precise training, reconsiderations concerning the training set as well as possible postprocessing steps are inevitable for a practical detector based on this approach.
Microfluidic flows are prevalent everywhere in modern technologies. From lab-on-a-chip devices, to inkjet printing, to system biology, and in wetting and de-wetting phenomena for coating technologies, their application is ubiquitous. In this study we are interested in developing a novel framework with reduced dimensionality for open microfluidic problems. More specifically, we are interested in studying thin film flows using depth averaged viscous shallow-water equations with capillary forces and fluid-wall interactions included. We adopt the mesoscopic lattice Boltzmann method (LBM) to solve for the shallow water system.
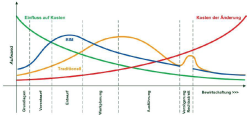
The introduction of digital planning methods is a constant, fast-changing process.For engineers, it is important to always be up-to-date to meet the requirements of the clients.In the course of this master thesis, existing processes in the planning phase and in the engineering office itself are to be identified which can be optimized by the use of BIM.Through a fundamental research on the current dissemination status of BIM, nationally and internationally, as well as through the comparison of conventional planning and BIM planning, the foundation for an implementation strategy is to be laid.A specific example is carried out on the basis of a completed infrastructure project done at an engineering office.

Recently, advances in the field of the so-called wire robot technology offer new prospects for the automation of large-scale processes. This thesis presents a simulation-based approach to analyze the technical and economic feasibility of wire robots for automated construction in future investigations. Masonry buildings are considered as an appropriate application case due to repetitive construction procedures and high demands concerning quality as well as accuracy of construction. A simulation model representing the fundamental mechanics of a wire robot is created including process-relevant objects and interactions. Special focus lies on creating collision-free motion profiles which can be exported to the robot control system and may serve as a basis for path planning. Building information models provided in the IFC format are used to set-up the simulation model and to prepare the required input data.
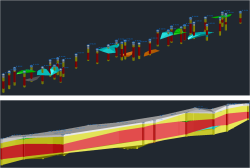
The aim of this thesis is to investigate the way to create a digital 3D-Subsoil-Model by using borehole data. Further, the usability if the used methods and possible benefits to the building industry should be analyzed. In the beginning, the thesis focuses on building information modeling and borehole technology to show the possible ways of generating 3D-Model by using borehole data. Following, the thesis examines the used add-ons for AutoCAD Civil-3D to create and to use a 3D-Subsoil-Model. Concluding, the model quality as well as the modeling efficiency is analyzed and evaluated.
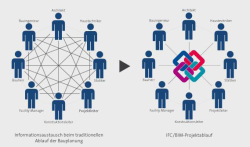
This master thesis illustrates the importance of the Building Information Model for the German construction industry. The analysis of the conventional approach and the BIM based approach are compared to show the advantages and disadvantages of both methods. Using the BIM based software iTWO, a prototypical implementation is created to calculate quantity determination according to given construction guidelines. Furthermore, a strategy on the use of BIM is proposed for production planning and execution.